The Need For Digital Twin Safety
- Raimund Laqua
- Feb 7, 2024
- 2 min read
Updated: Jun 1, 2024
Digital twins are virtual counterparts of physical entities that merge real-time data from sensors and IoT devices with sophisticated analytics and simulation, facilitating monitoring, analysis, and optimization of operations and assets.
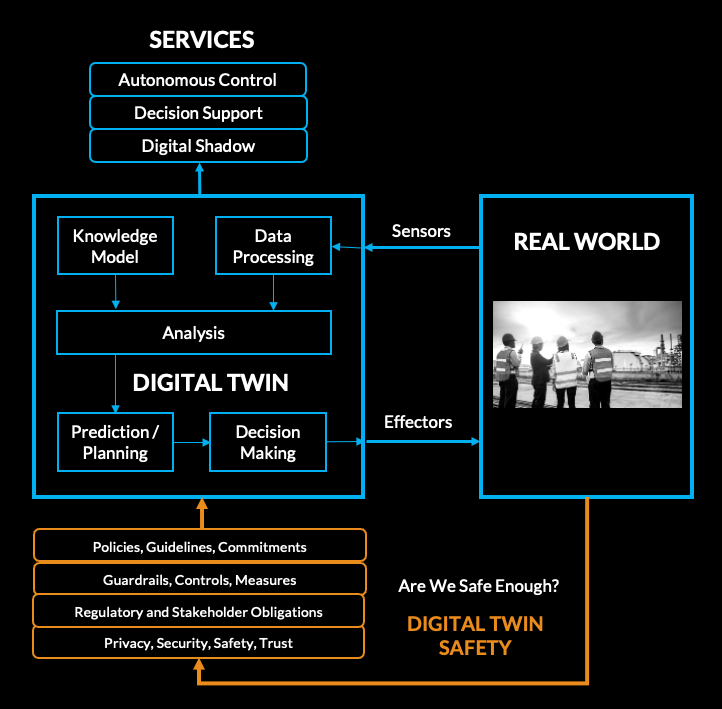
Alongside benefits of Digital Twins, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) introduces additional considerations and risks commensurate with how digital twins are used either as a Digital Shadow, Decision Support, or for Autonomous Control:
Digital Shadow:
Digital twins provide real-time representations of physical entities, offering insights without direct interaction.
AI algorithms enhance the analysis of data within digital twins, but they also introduce the risk of bias or errors if not carefully trained and validated. Moreover, AI-driven decisions may be opaque, making it challenging to understand their rationale and assess their reliability.
Decision Support:
Digital twins can serve as decision support tools by providing actionable intelligence through advanced analytics and simulation.
AI algorithms within digital twins enable predictive modeling and optimization, but they may also amplify errors or biases present in the data. Additionally, complex AI models may lack interpretability, hindering decision-makers' ability to trust and understand their recommendations.
Autonomous Control:
Digital twins in its most advanced state enable autonomous control by acting on decision-making based on real-time data and predictive insights.
AI algorithms drive autonomous actions within digital twins, enhancing efficiency and responsiveness. However, they also introduce risks of malfunction or adversarial attacks, potentially leading to unintended consequences or safety hazards. Additionally, AI-driven autonomous systems may face ethical considerations regarding accountability and transparency in decision-making.
While the integration of AI enhances the capabilities of digital twins, it also introduces considerations related to algorithmic bias, interpretability, and system reliability. Addressing these considerations requires rigorous validation, transparency, and ethical oversight to ensure the responsible and effective use of AI within digital twin technologies across diverse applications and industries.
Digital Twin Safety
In light of the risks associated with digital twins, particularly when integrating Artificial Intelligence, establishing robust safety programs is imperative to protect the public and effectively contend with potential risks.
A comprehensive Digital Twin Safety Program should encompass rigorous risk assessment, validation, and continuous monitoring mechanisms. This involves identifying and evaluating potential risks arising from data inaccuracies, algorithmic biases, cybersecurity threats, and system malfunctions. Additionally, the safety program should prioritize transparency and accountability in decision-making processes, ensuring that stakeholders understand the basis of AI-driven actions and can intervene if necessary. Regular audits and evaluations of digital twin systems are essential to identify emerging risks and adapt mitigation strategies accordingly.
In addition, collaboration between industry stakeholders, regulatory bodies, and technology developers is crucial to establish standards, guidelines, and best practices for the responsible deployment of digital twin technologies that use machine intelligence capabilities.
By implementing robust safety programs, organizations can mitigate risks, safeguard public welfare, and foster trust in the use of digital twins across various domains.

